Transgenic Animals Definition Biology

They may also be engineered to have advantageous or useful traits.
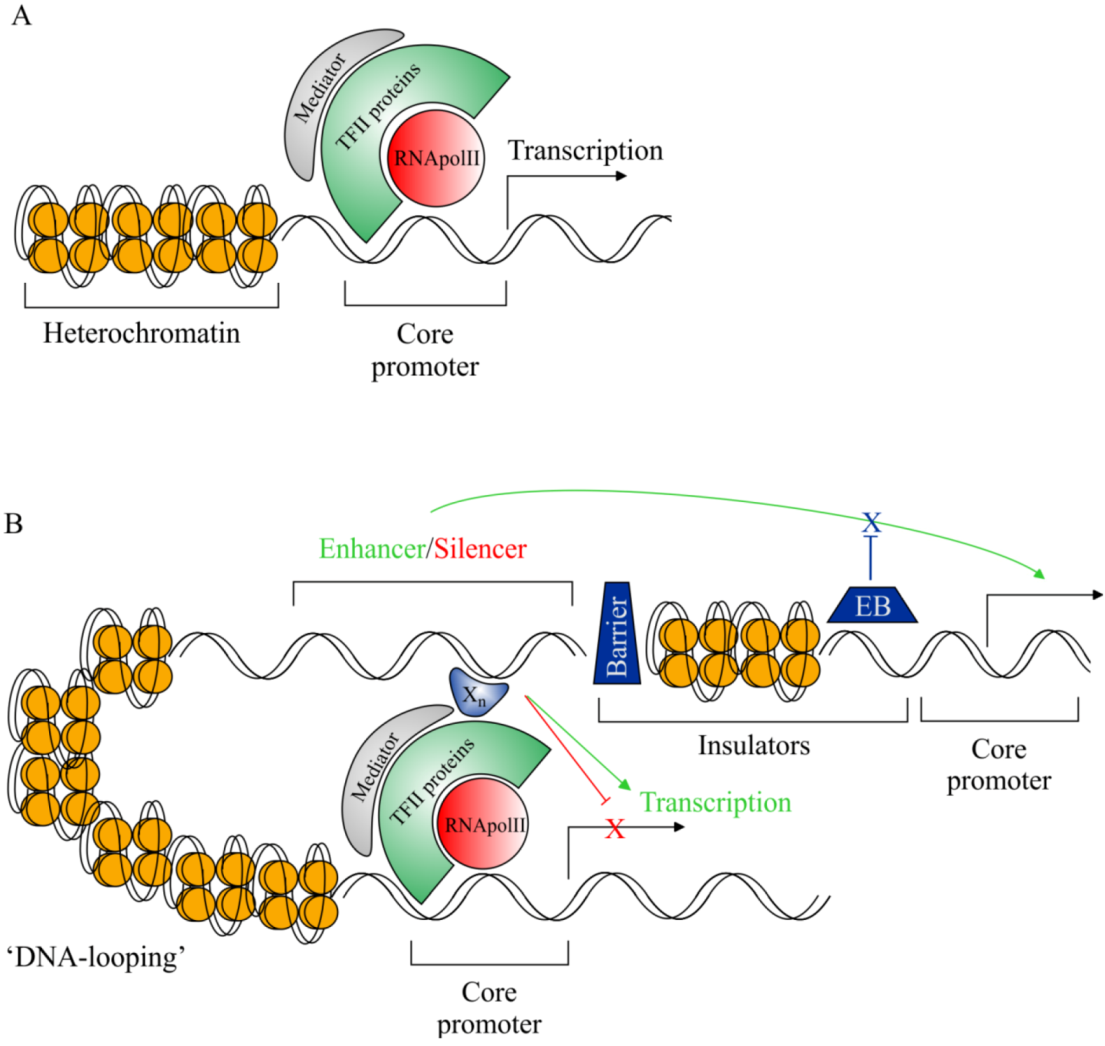
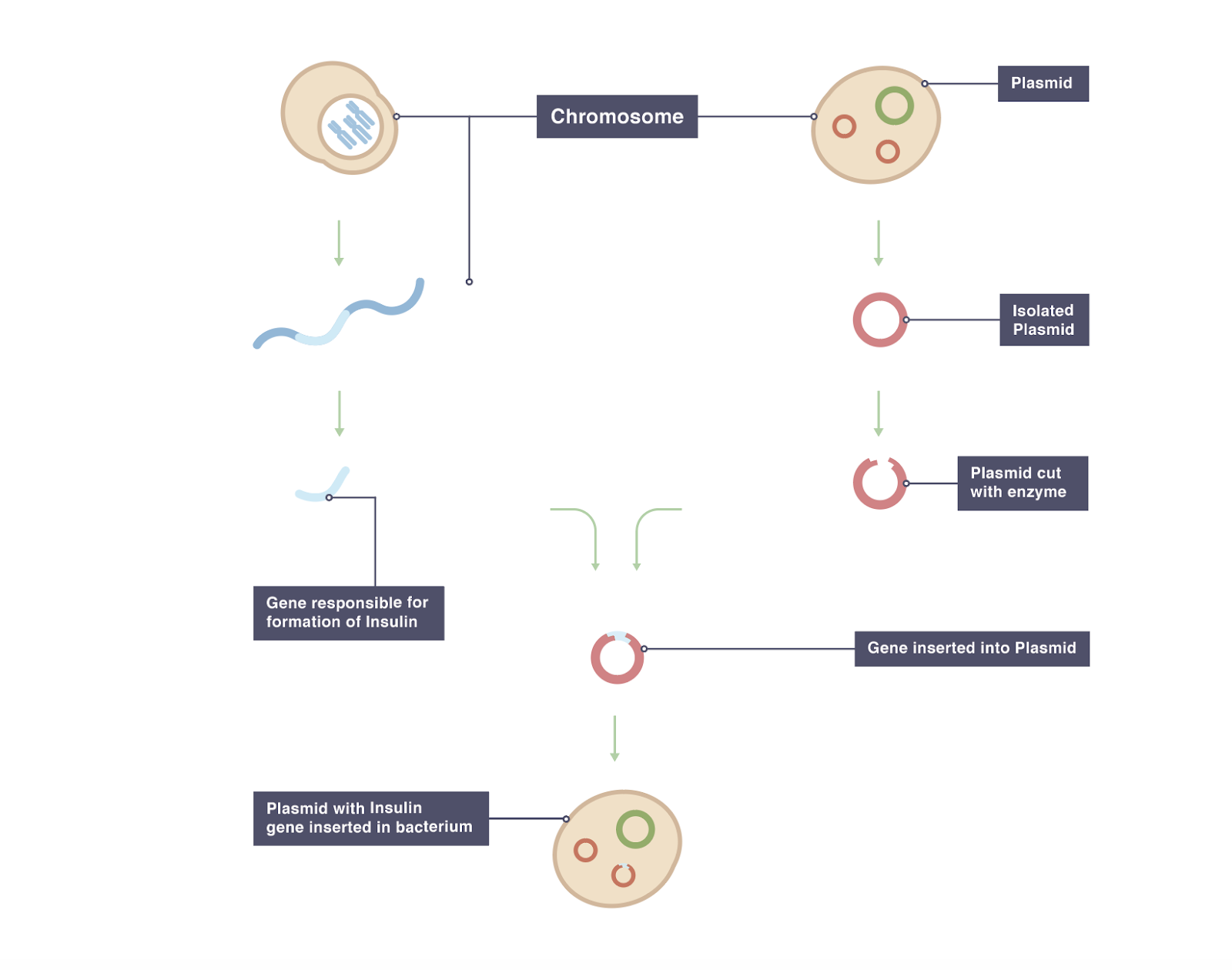
Transgenic animals definition biology. A transgenic animal is one that carries a foreign gene that has been deliberately inserted into its genome. The foreign gene is constructed using recombinant DNA methodology. Theoretically all living beings can be genetically manipulated.
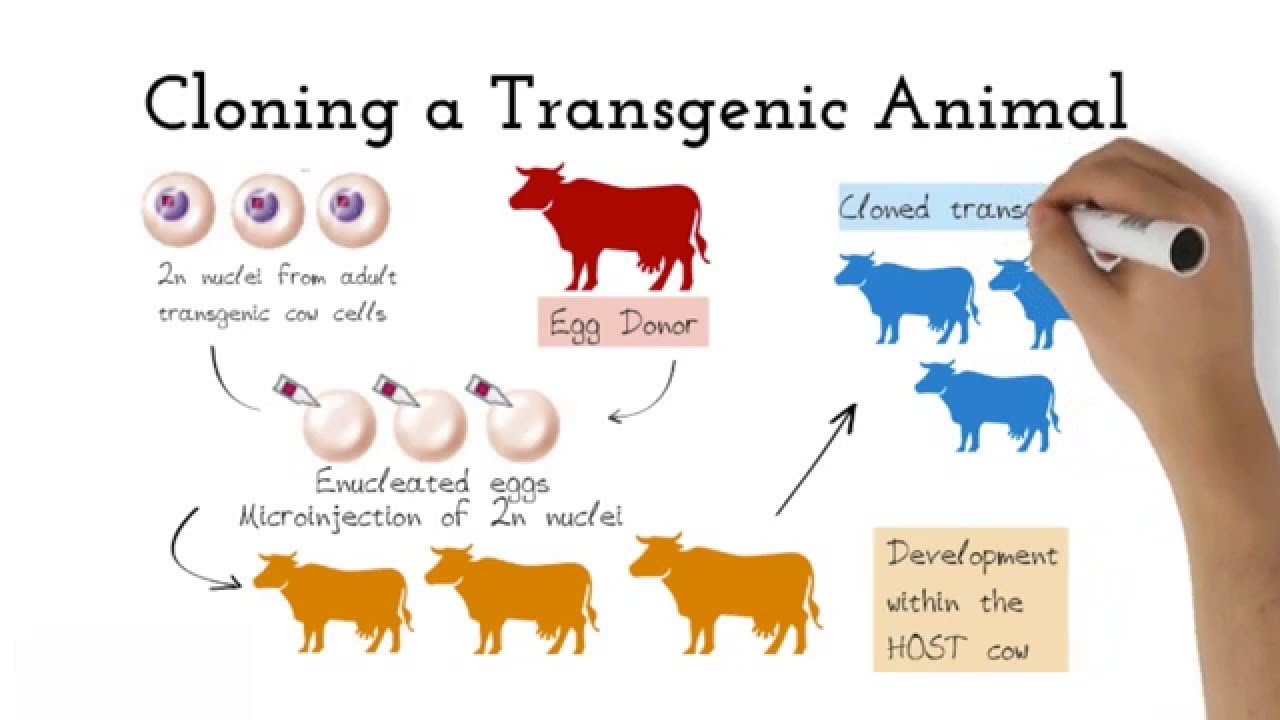
Transgenic animals are those that have been genetically modified. Transgenesis is the process by which mixing up of genes takes place. Foreign genes are inserted into the germ line of the animal so it can be transmitted to the progeny.
Transgenic animals have also been produced to study animal biochemical processes and human diseases or used to produce pharmaceuticals and other proteins. Transgenic animals definition biology. The first successful transgenic animal was a mouse6 A few.
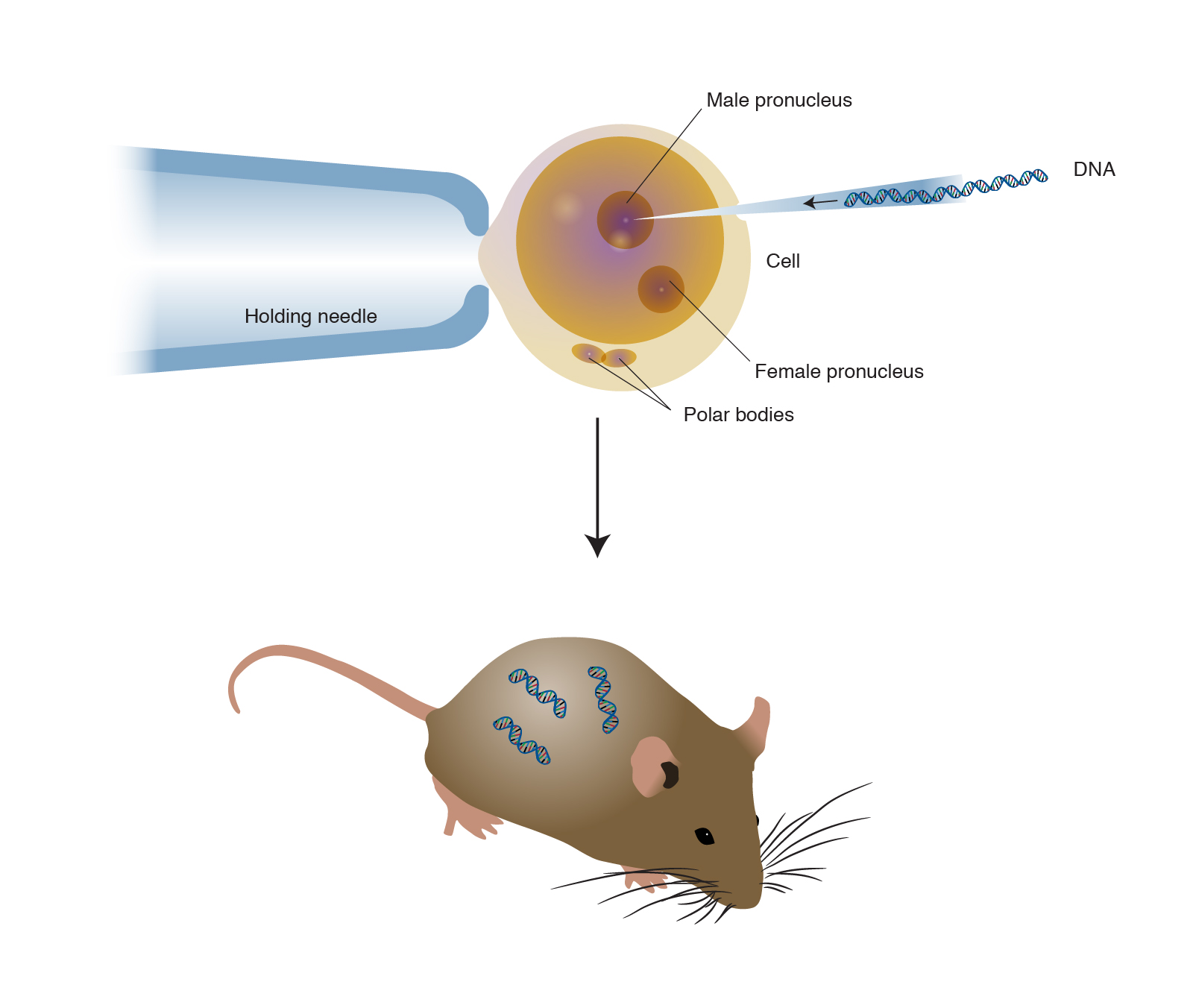
The foreign DNA or transgene that is transferred to the recipient can be from other individuals of the same species or even from unrelated species. Arise from pluripotent stem cells. BTransgenic animals are made that carry genes which make them more sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals.
Transgenic plants can be made by introducing foreign DNA into a variety of different tissues. Transgenic animals are specially designed to study the role of genes in the development of certain diseases. Sheep goats pigs cows rabbits rats mice fish insects parasites and even humans have previously been used in this modification process.
Transgenics describes the process of introducing foreign deoxyribonucleic acid DNA into a host organisms genome. Theoretically all living beings can be genetically manipulated. Full article A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been changed to carry genes from other species.

_1602913203_391831-5.jpg)