Deep Ocean Animals Adaptations

Filter feeders are oceanic animals that feed on floating organisms by straining them out of the moving water.
Deep ocean animals adaptations. The photic zone also known as the sunlight zone is the uppermost layer of a lake or ocean that receives sufficient sunlight to support aquatic plant life. The dense ocean water is filled with tiny floating organisms. In anglerfish Linophryne Fig 24 the light is used as a.
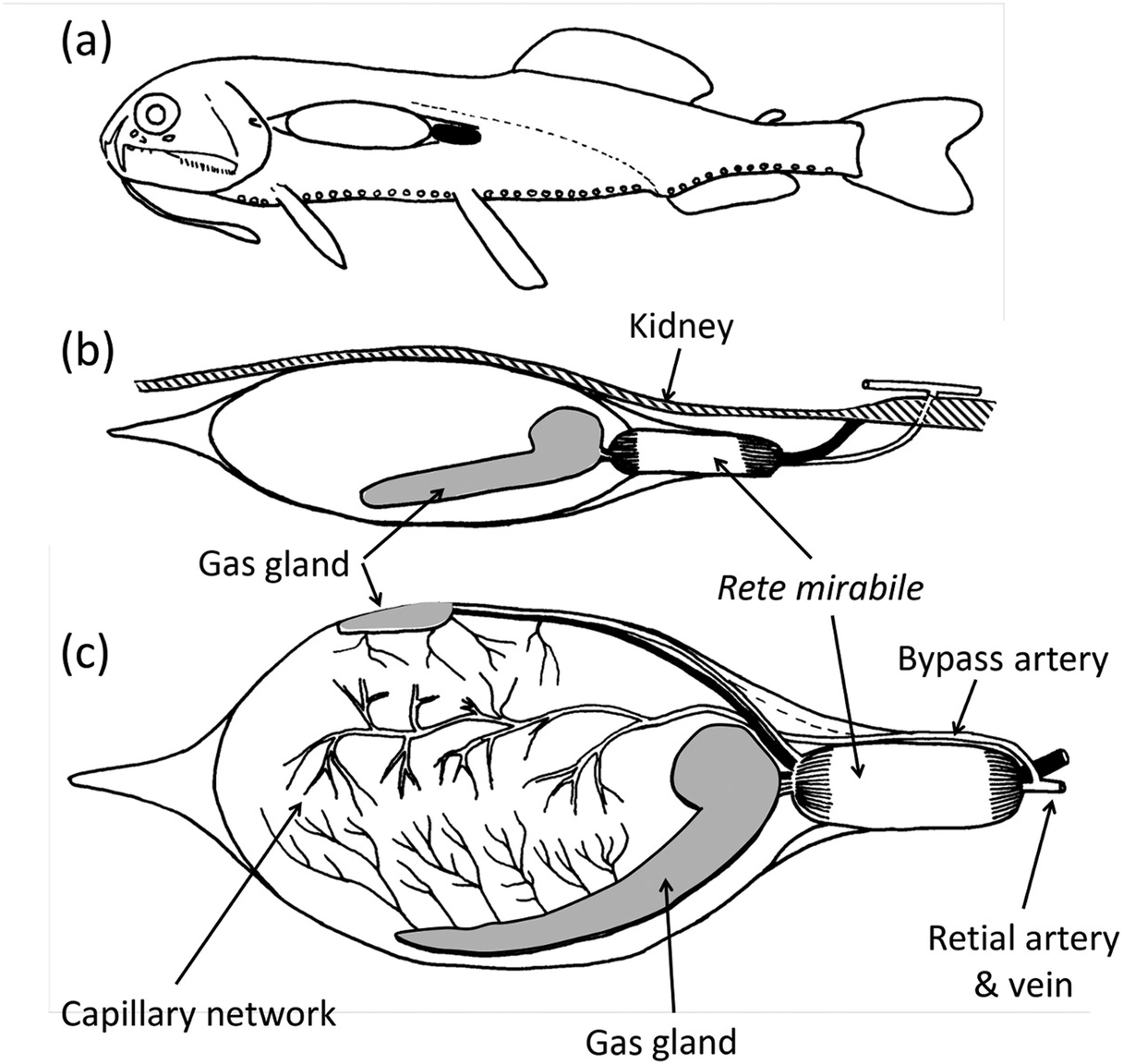
These creatures have several adaptations like compressible lungs lung-like swim bladders etc to help them overcome the high water pressure in their deep-water environment. Coastal plants need special adaptations to survive. Deep-sea creatures are animals that live below the photic zone of the ocean.
Many animals make their own light called bioluminescence to communicate find mates scare predators or attract prey. Eyes contain a type of light receptor called rods. Deep-sea hot springs recently discovered along the axes of ridge and rise systems support unique communities of deep-sea animals and bacteria.
5 Other Adaptations of Deep Sea Creatures. For example many types of seaweed attach. Have students identify animal adaptations in.
Introduction to Deep Sea Adaptation. Contains a chart for students to label the different zones of the ocean as well as a chart to keep track of different animalcreature adaptations in different zones. The intertidal zone the pelagic zone and the abyss.
In this lesson students consider the diversity of animals in the deep ocean noting similarities and variations in how animals have adapted to their deep ocean environment. The benthic division includes Bathyal 200 m 400 m Abyssal. Animals adapt to their environments to help them survive.