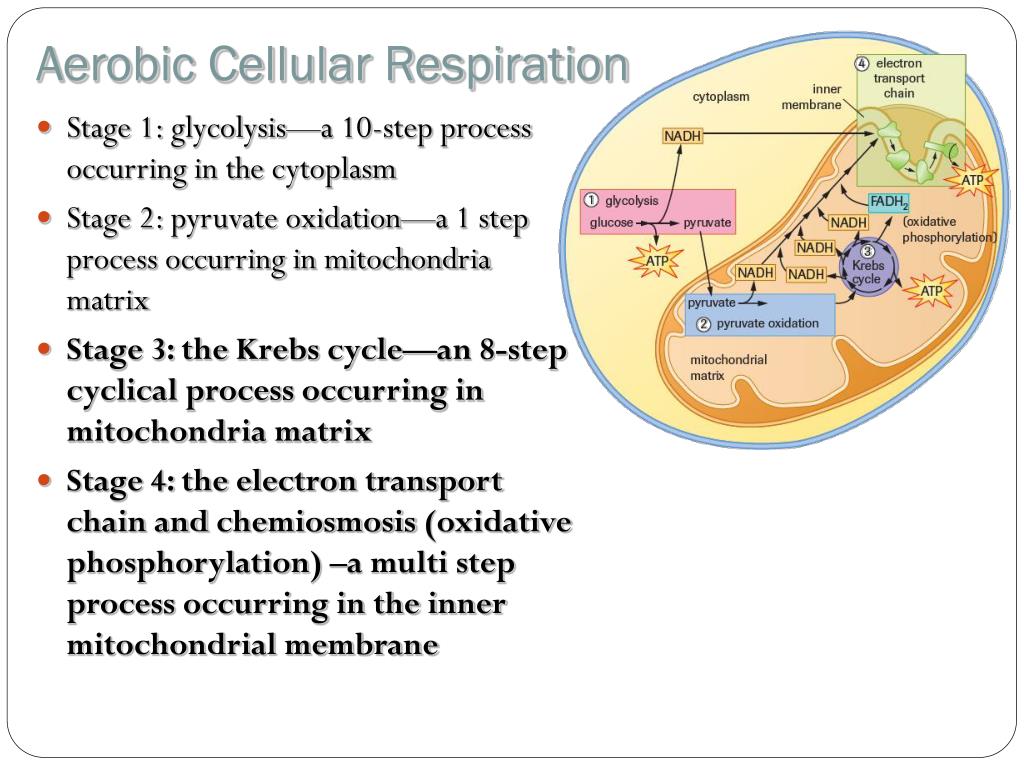
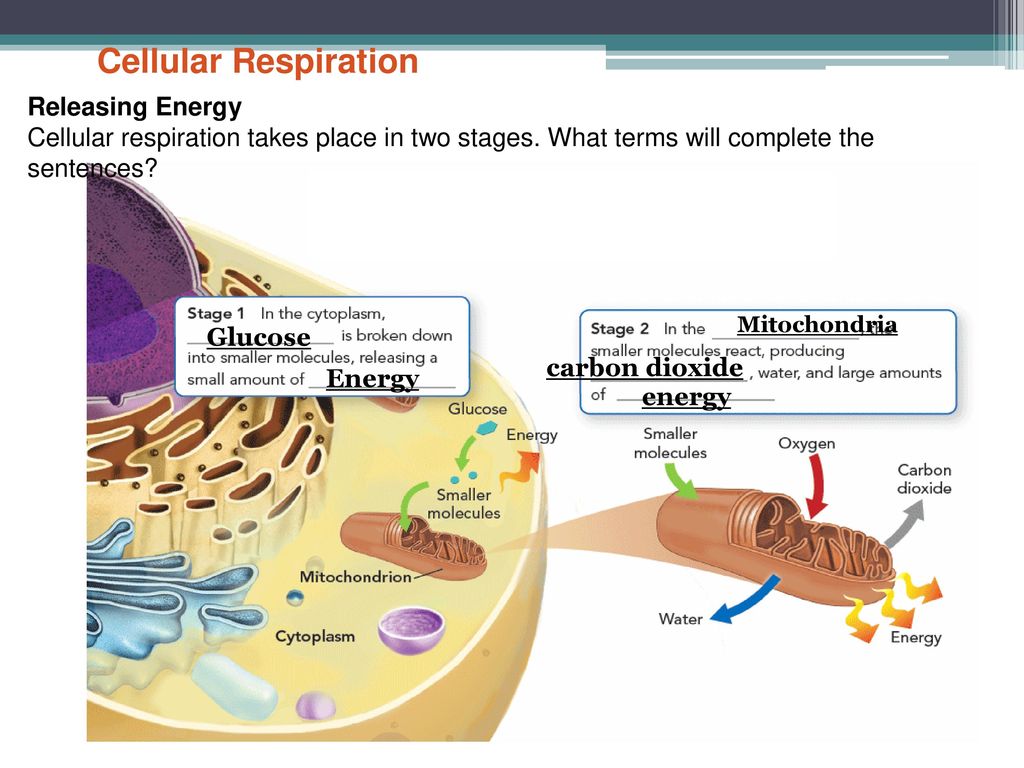
Cellular Respiration Takes Place In Two Stages
The oxygen is not essential for glycolysis.
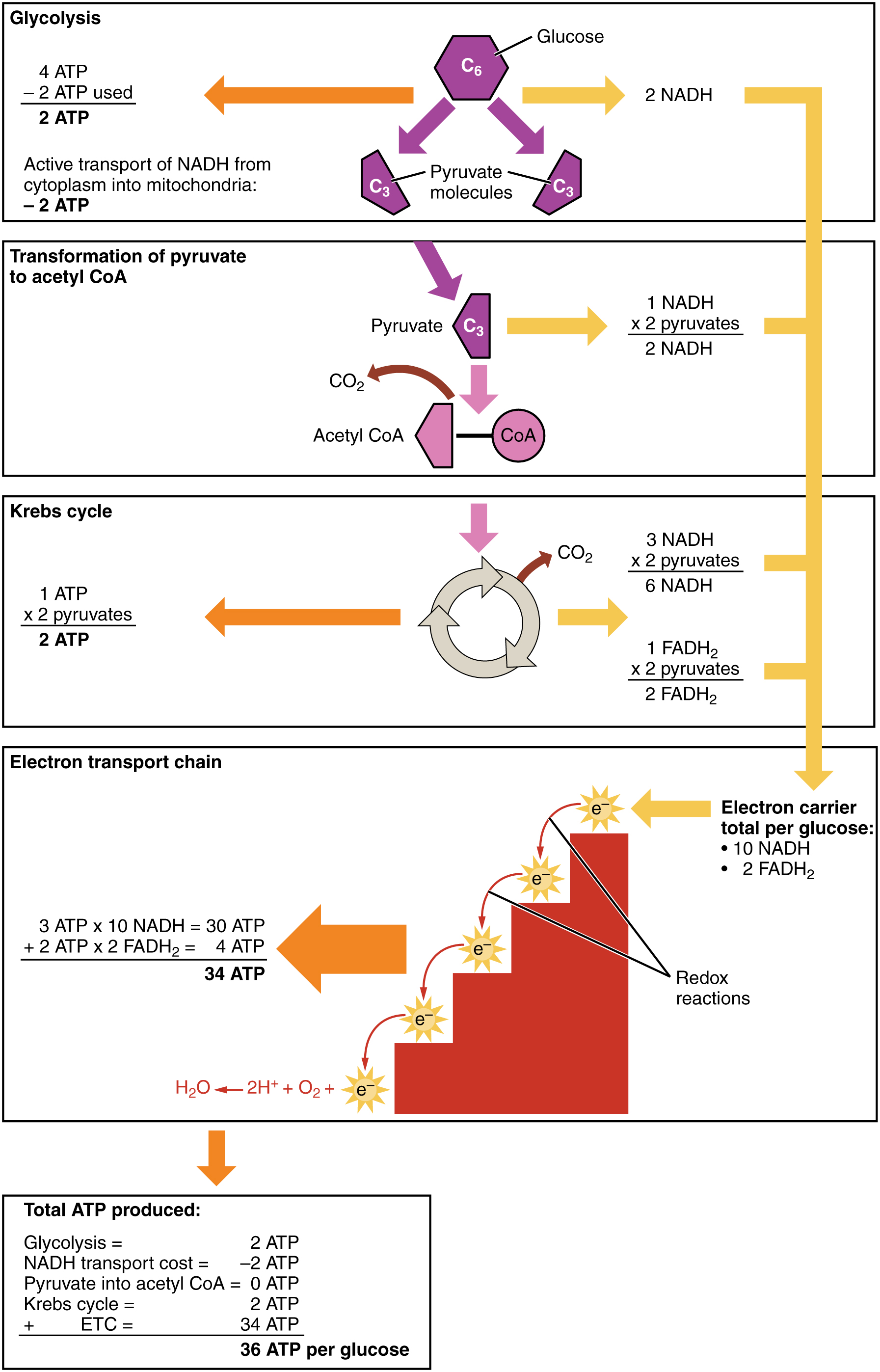
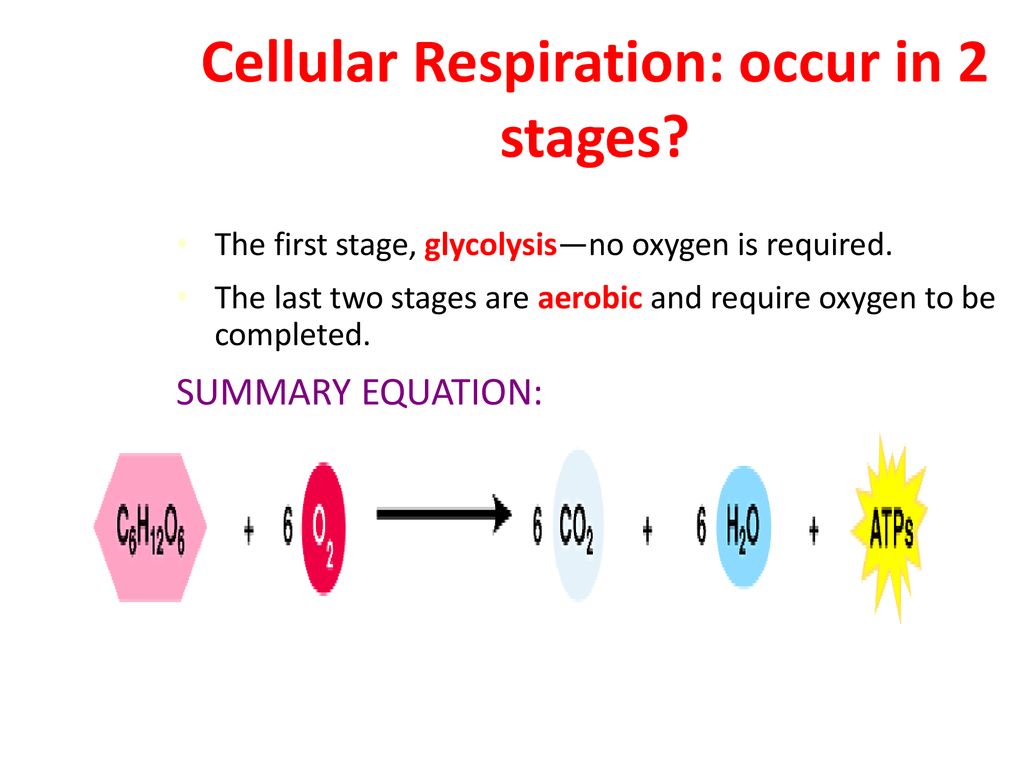
Cellular respiration takes place in two stages. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. Anaerobic respiration takes place in the cell cytoplasm. Based on the oxygen demand cellular respiration is divided into- Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration.
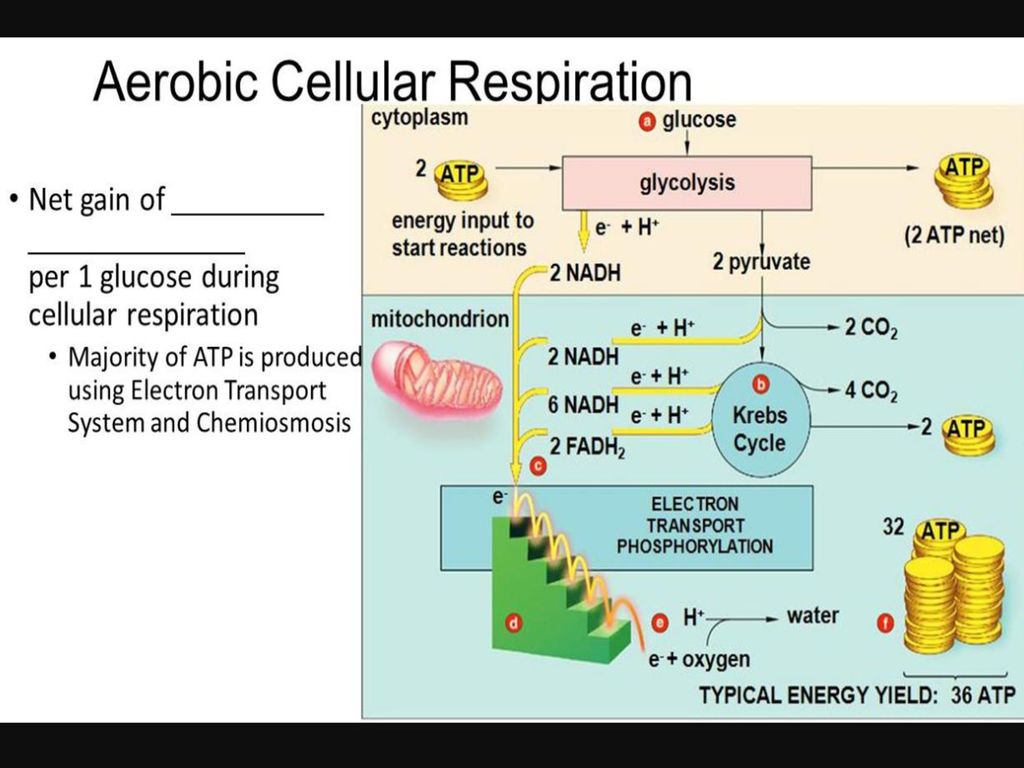
There are three main stages of cellular respiration. This includes the entry of oxygen and the exit of carbon dioxide from the cells. The net effect is that it splits 6 carbon rings of glucose into two 3-carbon molecules called pyruvic acids.
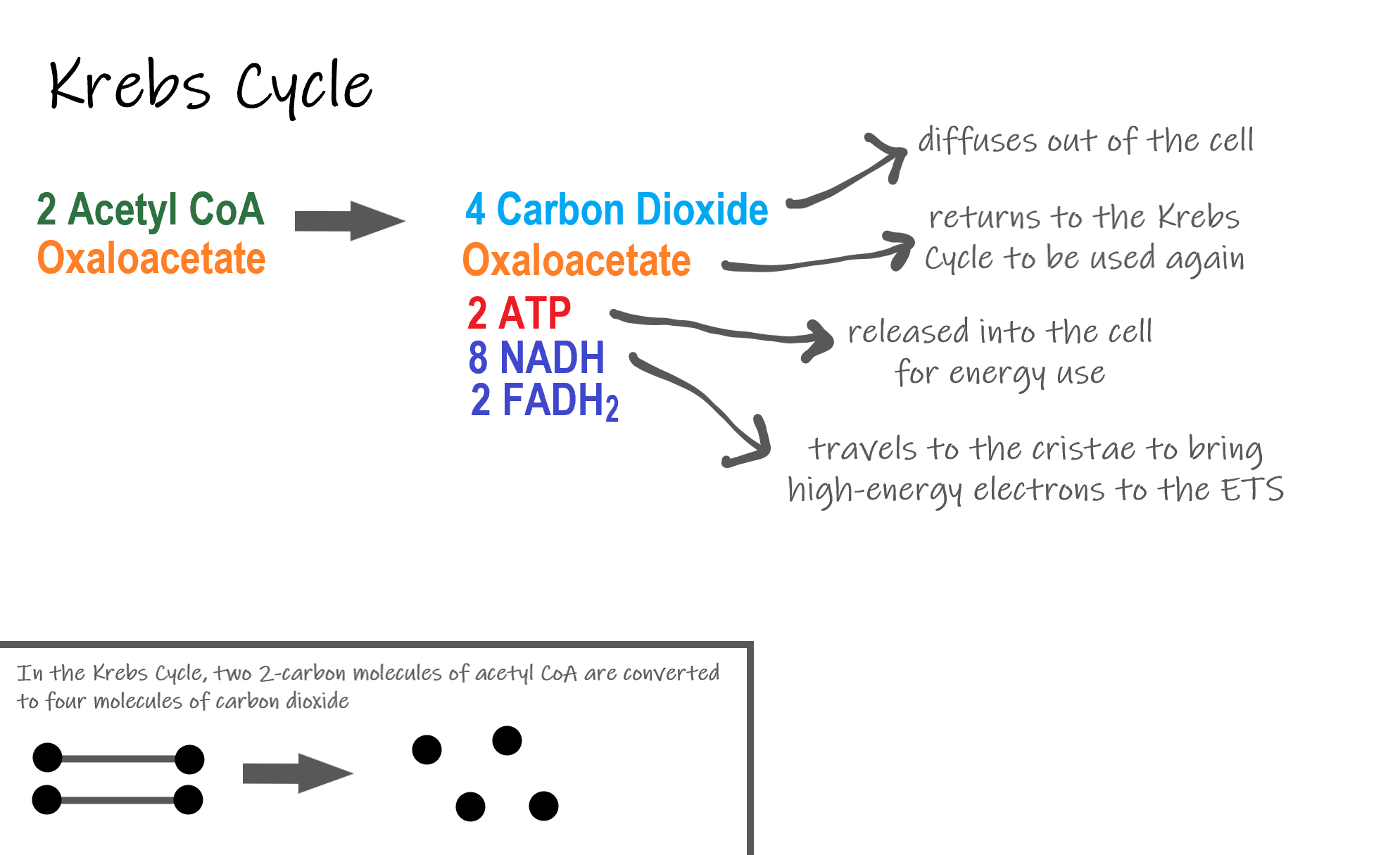
Glycolysis the citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain. Respiration In cellular respiration a two-carbon molecule combines with a four-carbon molecule to form citric acid as part of. The three stages of aerobic cellular respiration are.
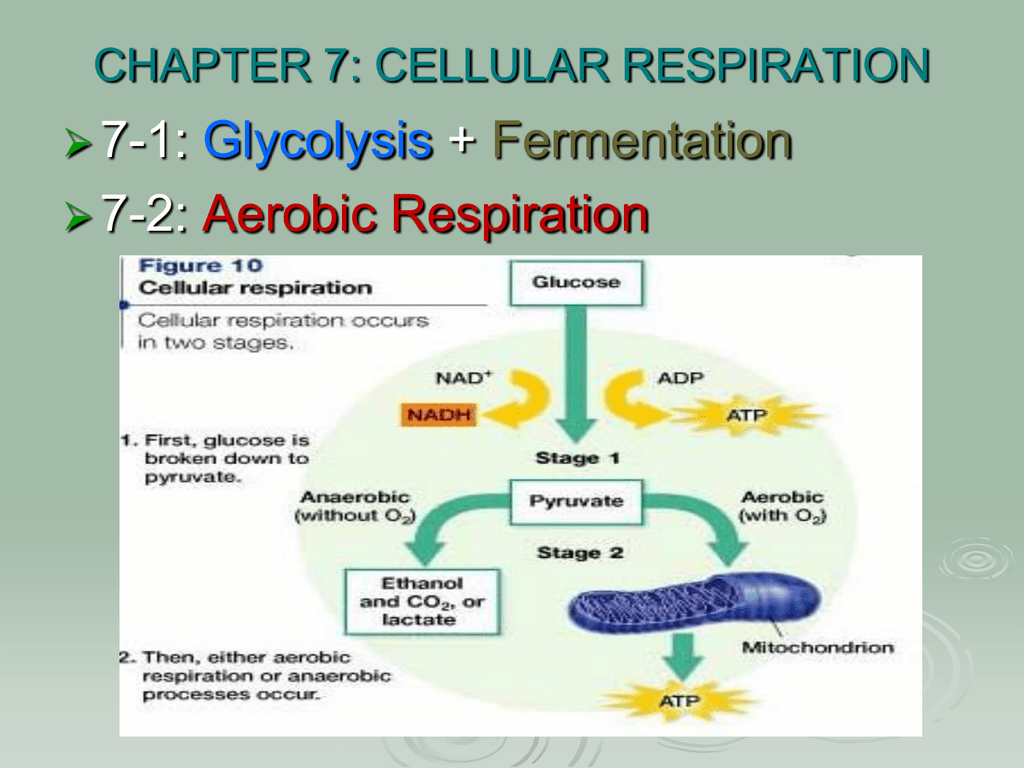
The stages in aerobic respiration are. There are three main stages of aerobic respiration glycolysis the Krebs Cycle and the electron transport chain each of which deserves an entire article all to itself but when looking at the overall process of cellular respiration we will only look at these stages at a somewhat basic level leaving out the specific details of every chemical reaction in each stage. Glycolysis generates 2 ATP.
Glycolysis is an anaerobic. The Krebs Cycle which takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria. This pathway is anaerobic and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
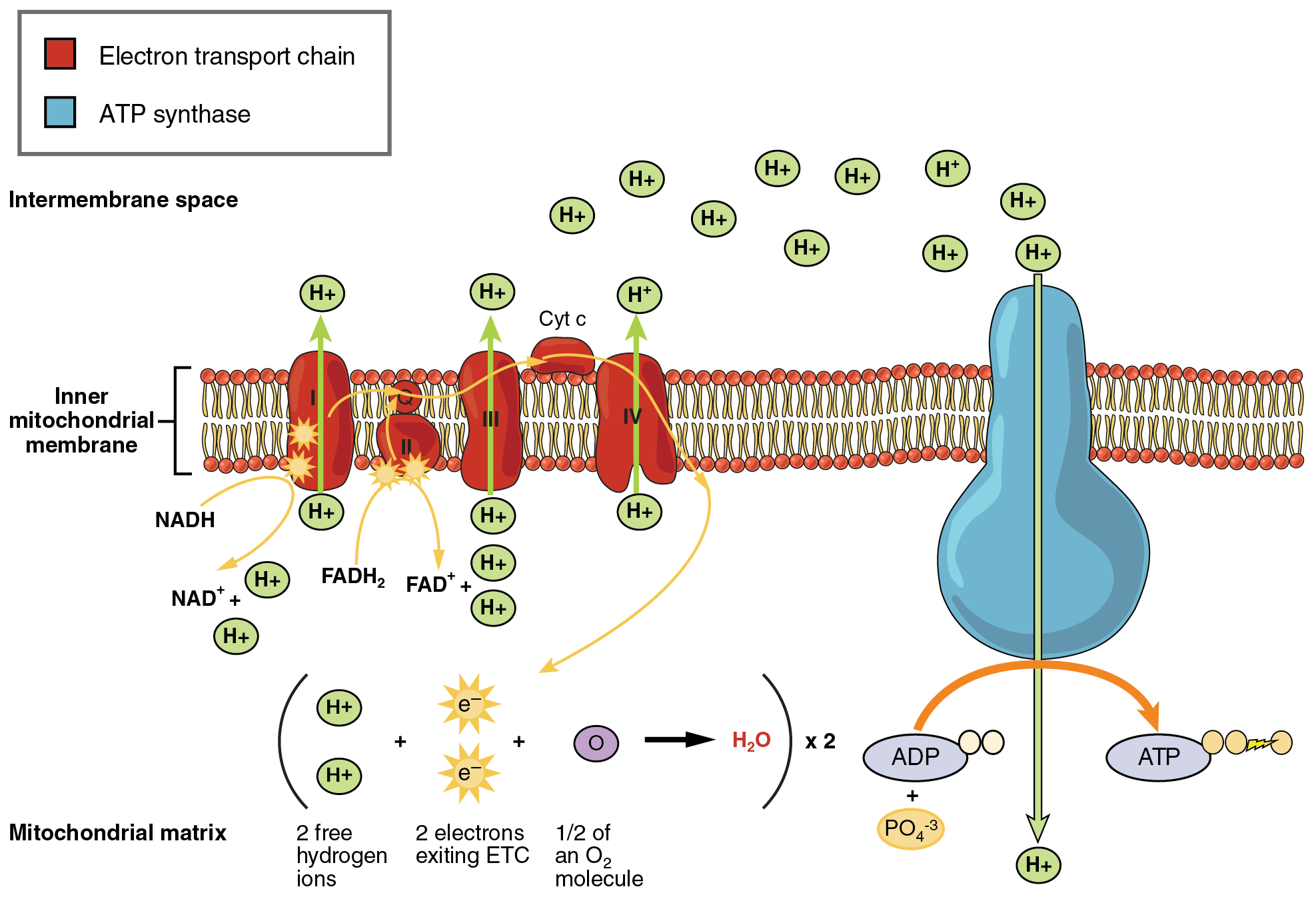
Glycolysis is an anaerobic process. Are transferred to molecules of NAD to produce two molecules of NADH. Curbs cycle or citric acid cycle.


/respiration-58b9a1d93df78c353c0e3e0f.jpg)







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration_3-58b9a5415f9b58af5c839e04.jpg)
