Cellular Respiration Formula With States
Explain why aerobic cellular respiration results in 36 ATPs per glucose in eukaryotic cells and 38 ATPs per glucose in prokaryotic cells.
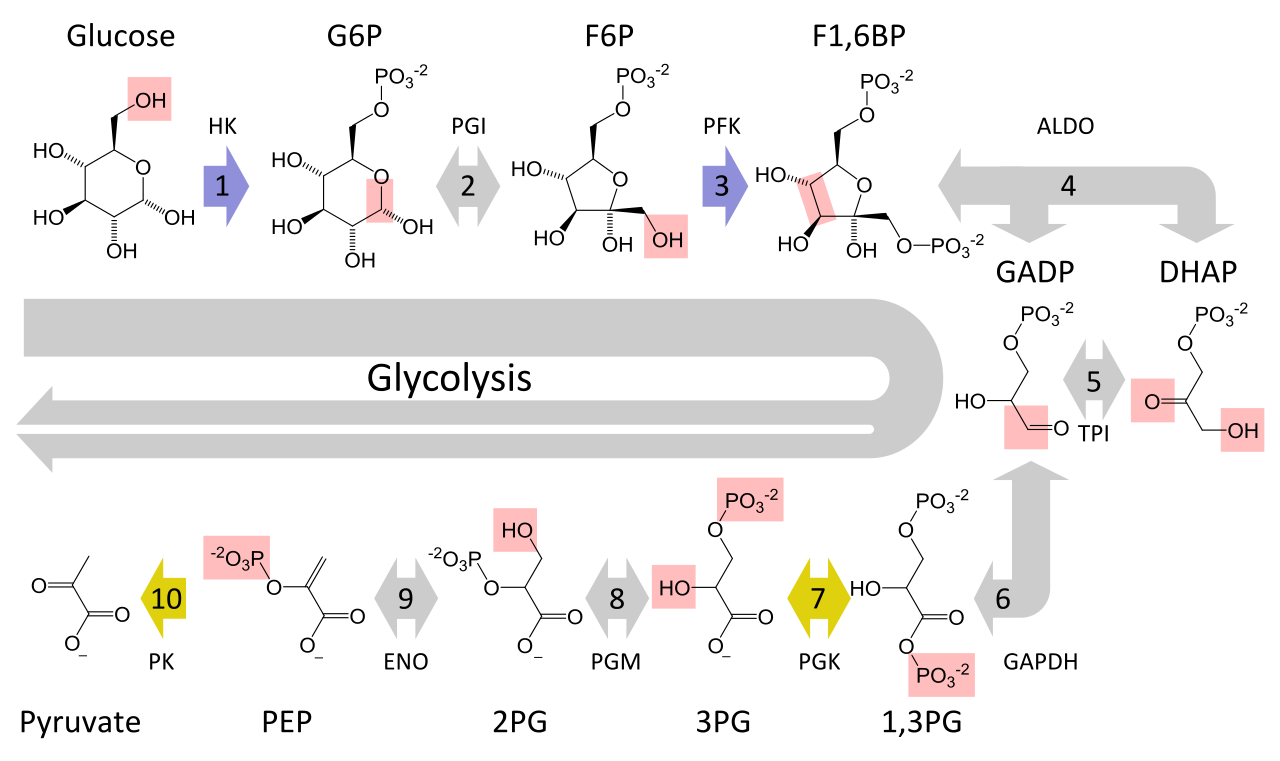
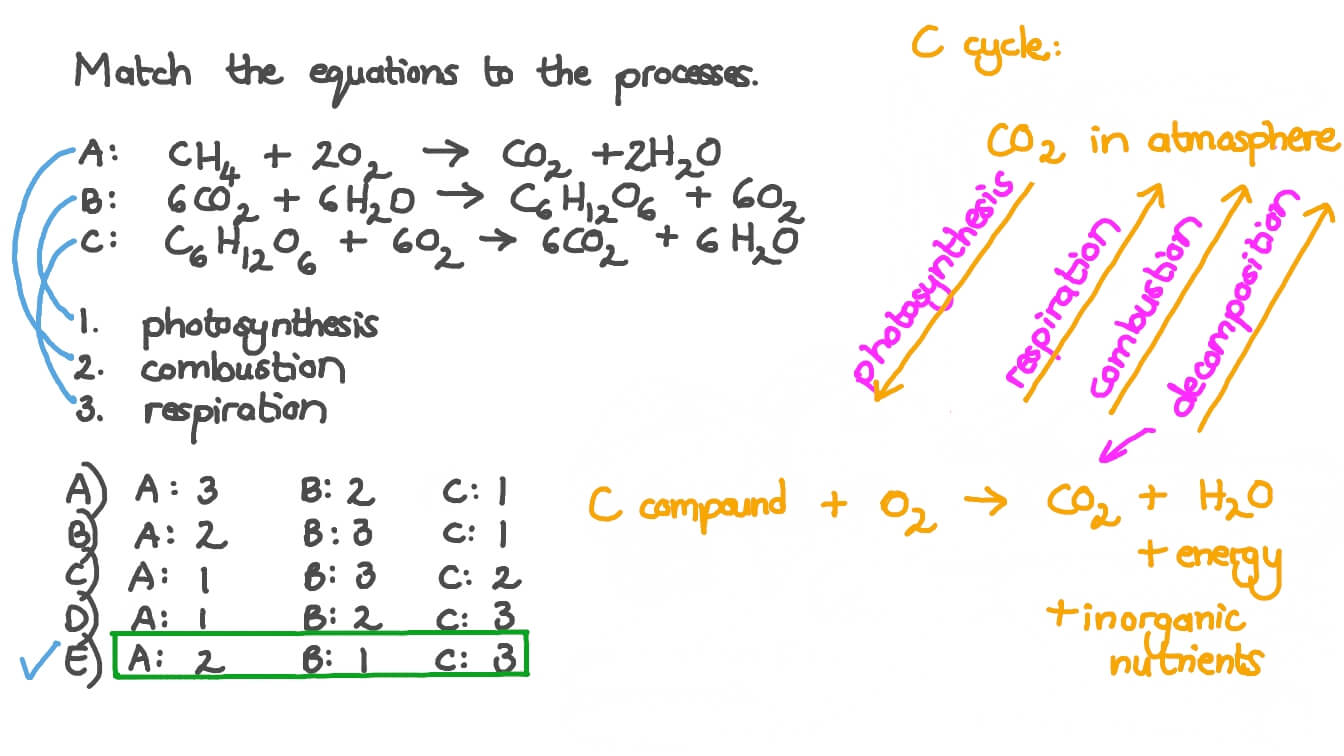
Cellular respiration formula with states. C_6H_12O_6 O_2 CO_2 H_2O energy. It is symbolized by the chemical formula of C 6 H 12 O 6 6O 2 6CO 2 6H 2 O C 10 H 16 N 5 O 13 P 3 also known as ATP. Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms convert the biochemical energy of nutrients into ATP.
Cellular respiration is a metabolic process consisting of a series of steps to convert chemical energy sugar into a usable form of energy ATP in the cell. Redox describes all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed. It is also known as a catabolic reaction as a large molecule like a carbohydrate is broken down into smaller molecules.
To unlock this lesson you must be a. However cellular or aerobic respiration takes place in stages including glycolysis and the Krebs cycle. Cellular Respiration Definition.
Glucose 6 oxygen 6 carbon dioxide 6 water ATP. Cellular respiration is a set of chemical reactions cells use to change the food we eat the water we drink and oxygen from the air we breathe into forms the cell can use as energy. ENE1L7 EK Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP.
Its overall chemical reaction of cellular respiration equation is simplified as. There are three main stages of cellular respiration. The stages of cellular respiration include glycolysis pyruvate oxidation the citric acid or Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation.
It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. The cellular respiration equation is a part of metabolic pathway that breaks down complex carbohydrates. A glucose molecule combines with 6 oxygen molecules producing 6 molecules of water 6 molecules of water and ATP.