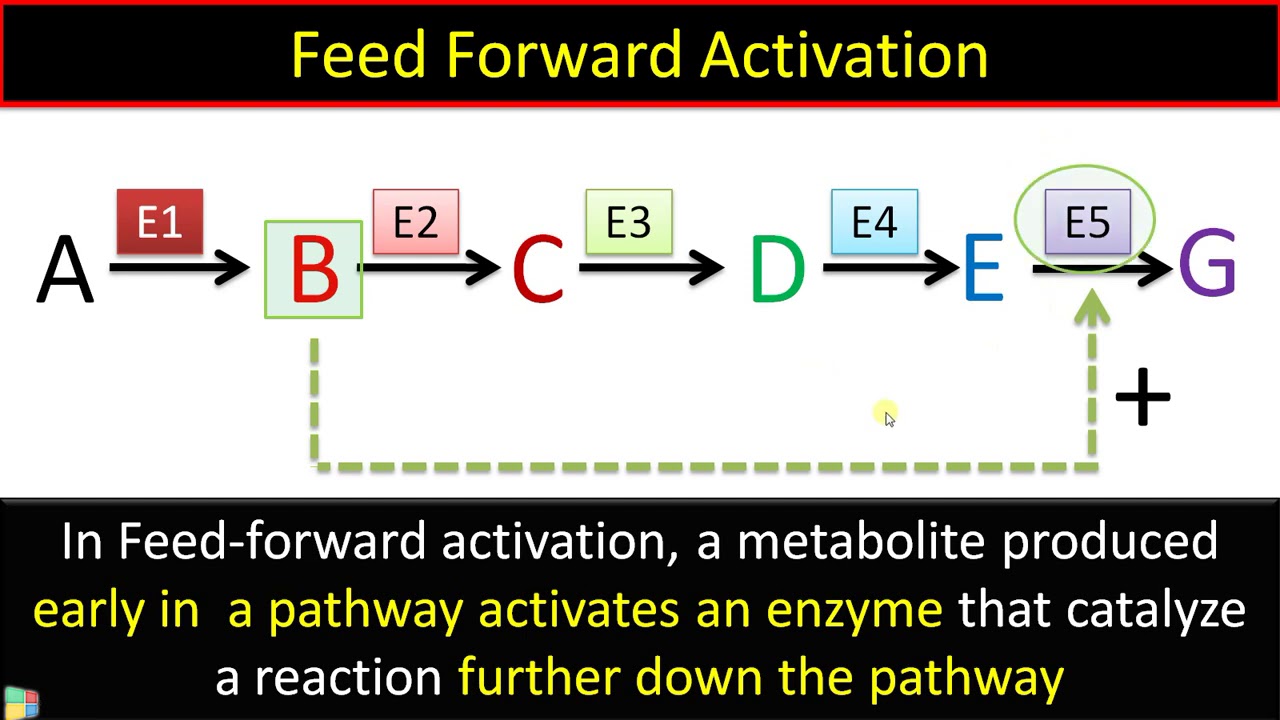
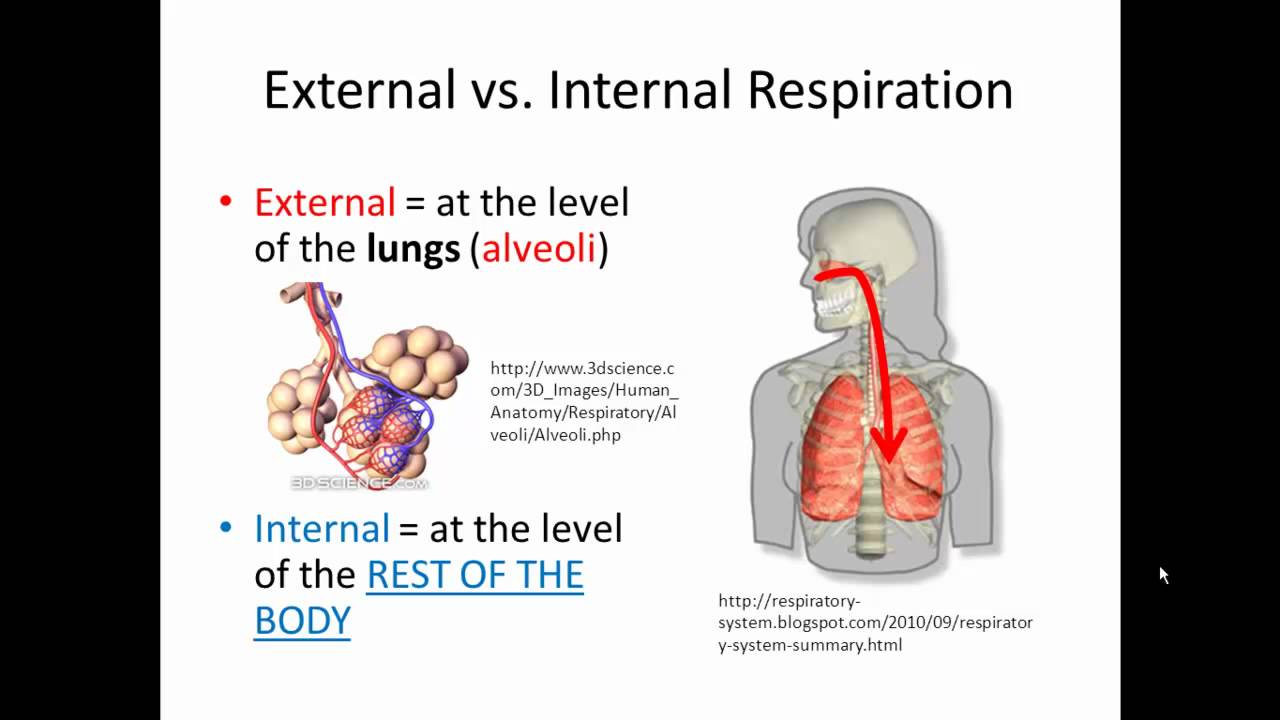
Cellular Respiration Equation Explained

Cellular respiration formula explained.
Cellular respiration equation explained. C_6H_12O_6 O_2 CO_2 H_2O energy The balanced equation is C_6H_12O_6 6O_2 6CO_2 6H_2O energy The equation expressed in words would be. Cellular Respiration gives both plant and animal cells the useable energy aka ATP that they need to do stuff. C6H12O6 6O2 --- 6CO2 6H2O 36 ATP.
Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products. The carbon dioxide is taken to the lungs where it is exchanged for oxygen. This is the balanced equation that yields energy.
The simplified formula for aerobic cellular respiration is. Cellular respiration is a process that is undergone in cells to break down molecules and produce ATP. Chemical structures of nad and nadh.
A short video covering the topic of cellular respiration including the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration prepared for a year 9 science. It is an exergonic reaction where high-energy glucose molecules are broken down into carbon dioxide and water. The chemical equation for aerobic cellular respiration is.
C6H12O6glucose 6O2 6CO2 6H2O 38 ATP. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate ATP and then release waste products. Cellular Respiration Definition.
In this reaction C6H12O6 6O2 are the reactants. In summary cellular respiration is a process that cells use to make energy. The energy released from the broken down molecules are a result of spontaneous catabolic reactions.